In Part one we setup the health check endpoints, now to add a frontend.
The Health Checks UI is best hosted in its own service as it can consolidate health checks for a number of services.
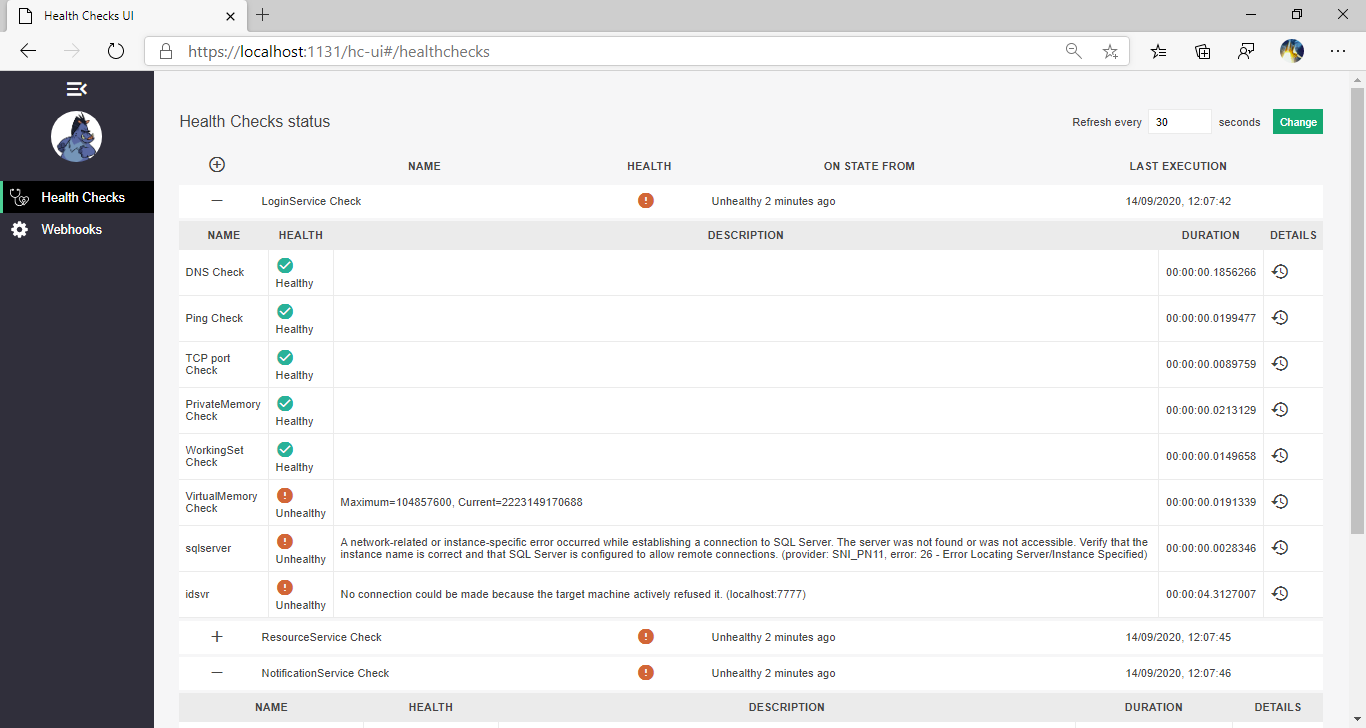
Adding the HealthChecks UI to the service involves adding 2 nuget packages, the main AspNetCore.HealthChecks.UI package and a storage provider, initially I have used the InMemory storage provider as I do not have the need to see historical data. There are also providers various databases including SqlServer and SQLite which can be used to persist the data.
<PackageReference Include="AspNetCore.HealthChecks.UI" Version="$(AspNetCoreHealthChecksUIVersion)" />
<PackageReference Include="AspNetCore.HealthChecks.UI.InMemory.Storage" Version="$(AspNetCoreHealthChecksUIVersion)" />
As the HealthChecks nuget packages will be used across all projects I have set the version numbers centrally in Directory.Build.props.
<AspNetCoreHealthChecksUIVersion>3.1.1</AspNetCoreHealthChecksUIVersion>
The HealthChecks UI can now be added to ConfigureServices and Configure in Startup.cs.
As I want to limit the access to the UI in the same way as I did for the HealthCheck endpoints I have the service listening on multiple ports and use RequireHost when configuring the endpoints to ensure the UI is only accessible internally.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services
.AddHealthChecksUI()
.AddInMemoryStorage();
services.AddControllers();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
app.UseHealthChecksUI();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllers();
endpoints.MapHealthChecksUI(config => {
config.UIPath = "/hc-ui";
}).RequireHost($"*:{Configuration["ManagementPort"]}");
});
}
}
Finally we need to tell the UI where to read the HealthChecks from, this can either be done in a configuration file
...
"https_port": 1131,
"Urls": "http://localhost:1130;https://localhost:1131;https://localhost:1132",
"ManagementPort": "1132",
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"HealthChecks-UI": {
"HealthChecks": [
{
"Name": "LoginService Check",
"Uri": "https://localhost:1116/hc"
},
{
"Name": "ResourceService Check",
"Uri": "https://localhost:5002/hc"
},
{
"Name": "NotificationService Check",
"Uri": "https://localhost:1179/hc"
}
]
}
...
or in code by adding settings to the AddHealthChecksUI method.
services.AddHealthChecksUI(setupSettings: settings =>
{
settings
.DisableDatabaseMigrations()
.AddHealthCheckEndpoint(name: healthCheckName, uri: healthCheckUri)
.AddWebhookNotification(name: webhookName, uri: webhookUri, payload: webhookPayload,
restorePayload: webhookRestorePayload)
.SetEvaluationTimeInSeconds(evaluationTimeInSeconds)
.SetMinimumSecondsBetweenFailureNotifications(minimumSeconds);
}).AddInMemoryStorage();
You can get the full working demo from my GitHub repo.